The Blog
What Are the Kinematical Consequences of Special Relativity?
Kinematical consequences arise from the need to rethink our understanding of space and time, especially when dealing with high-speed scenarios…
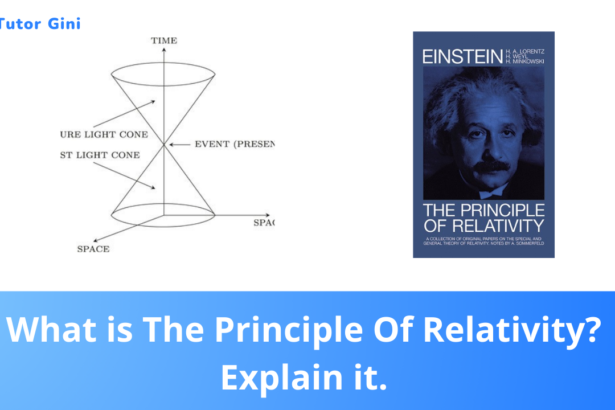
What is The Principle Of Relativity? Explain it.
The principle of relativity is not a new concept for us. We have seen that all frames of reference that…
Energy From The Nucleus – Explanation
Energy in various forms is available around us. Matter itself is a concentrate of energy. All atoms, molecules, nuclei, etc.,…
What are the properties and uses of nuclear radiation?
Alpha ray Beta ray Beta-plus ray Gamma ray Nuclear radiation, specially gamma ray, is used in medicine for cancer therapy…
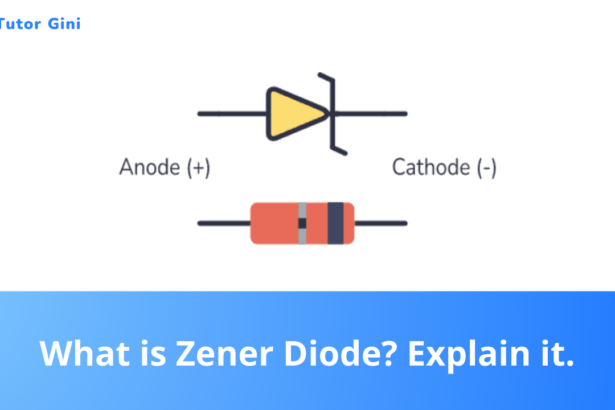
What is Zener Diode? Explain it.
If the reverse-bias voltage across a p-n junction diode is increased, at a particular voltage the reverse current suddenly increases…
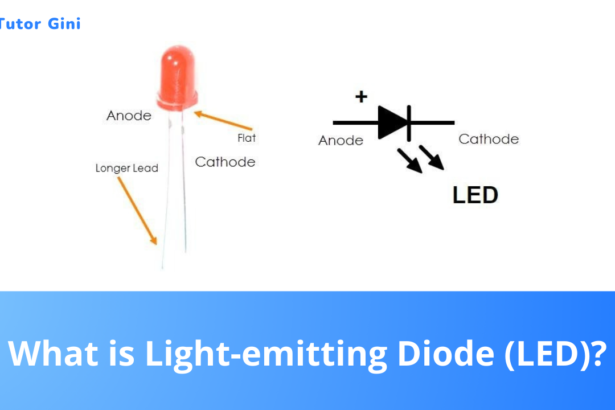
What is Light-emitting Diode (LED)?
When a conduction electron makes a transition to the valence band to fill up a hole in a p-n junction,…
What is Photodiode?
Photodiode is a p-n junction whose function is controlled by the light allowed to fall on it. Suppose, the wavelength…
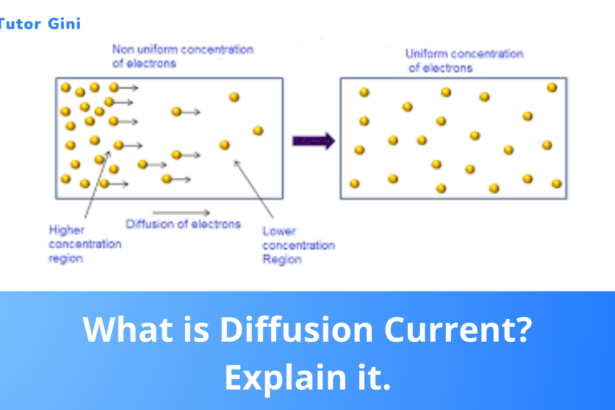
What is Diffusion Current? Explain it.
Because of the concentration difference, holes try to diffuse from the p-side to the n-side. In figure (45.11), this is…
What is Drift Current? Explain it.
Because of thermal collisions, occasionally a covalent bond is broken and the electron jumps to the conduction band. An electron-hole…
What are the properties and uses of X-rays?
As discussed earlier, X-rays are electromagnetic waves of short wavelengths. Accordingly, it has many properties common with light. Here are…