The Blog
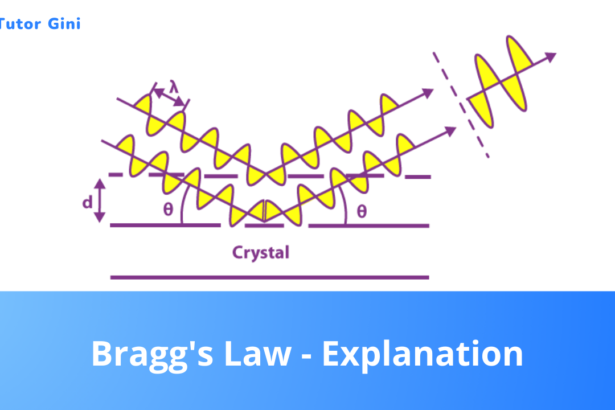
Bragg’s Law – Explanation
X-rays are electromagnetic waves wavelengths and may be diffracted by suitable diffracting centres. However, the diffraction effects are appreciable only…
What is soft and hard X-rays? what are the difference between them?
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, similar to visible light but with much higher energy. They’re used in various…
What is a laser used for?
Laser was invented in 1960. Since then, laser technology has greatly advanced and now lasers have widespread use in industry,…
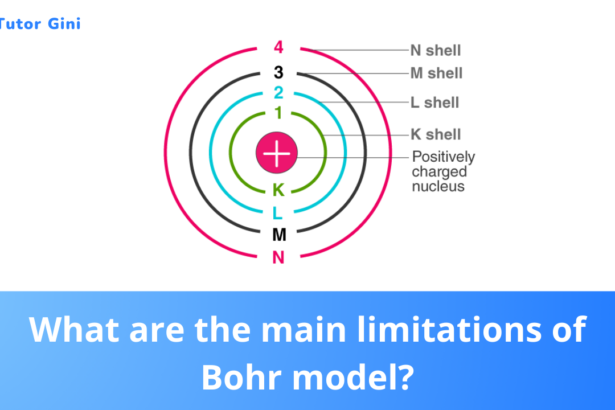
What are the main limitations of Bohr model?
Bohr's model was a great success at a time when the physicists were struggling hard to understand the discrete wavelengths…
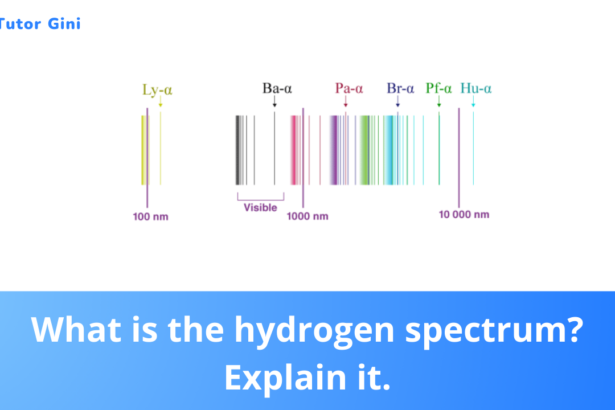
What is the hydrogen spectrum? Explain it.
Definition: The hydrogen spectrum refers to the specific pattern of light wavelengths emitted by hydrogen atoms when they are heated.…
What is Thomson’s model of the atom?
Thomson suggested in 1898 that the atom is a positively charged solid sphere and electrons are embedded in it in…
What is Diode Valve? Explain it.
A diode valve is a type of electronic component used to control the flow of electrical current. It allows current…
What is an Electron? Explain Discovery And Properties of an Electron.
An electron is a tiny particle that’s crucial in the atomic world. Imagine it as a super-small, negatively charged particle…
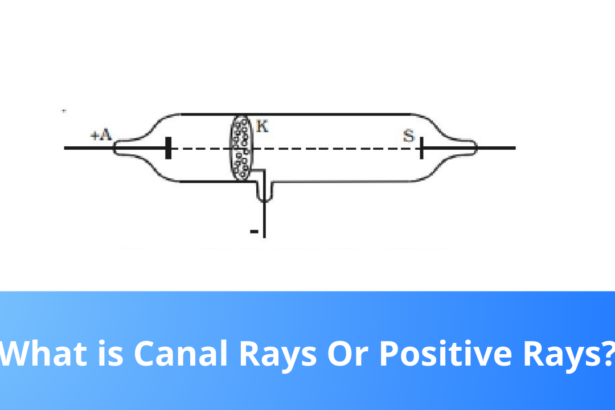
What are Canal Rays Or Positive Rays?
If the cathode of a discharge tube has holes in it and the pressure of the gas is around 1…
What Are Cathode Rays and What Are Their Properties?
When the pressure of the gas in a discharge tube is lowered, at a certain stage the Crookes dark space…